What Do Rod Cells Do
Rod cells vs Cone Cells
Similarities and Differences betwixt Rod Cells and Cone Cells
Rod cells and Cone cells are the 2 types of photoreceptor cells institute in the retina of eyes. These cells are capable of arresting light and converting the light into signals that can trigger a change in the membrane potential, which results in visual phototransduction. In other words, these cells help in vision in presence of light.
Rod cells: A blazon of photoreceptor cells in the centre found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina. Rod cells are responsible for vision in low light weather.
Cone cells: The second type of photoreceptor prison cell in the eye concentrated in the fovea of the retina. Cone cells are responsible for the vision in bright light and colour vision.
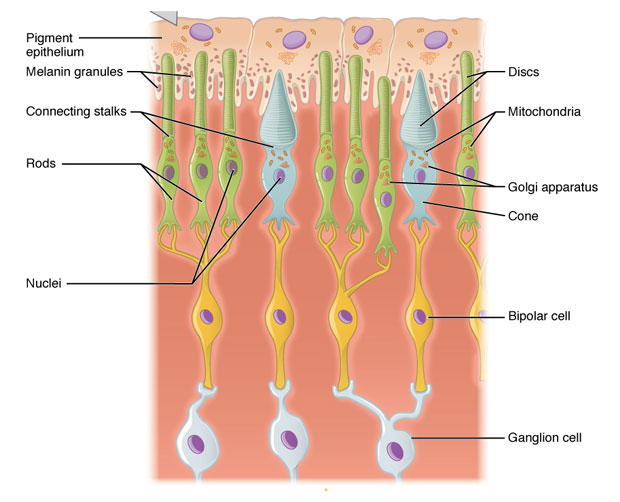
paradigm source: wikipedia
The present post explains the similarities and differences between Rod cells and Cone cells with a comparison table.
Similarities between Rods and Cones
Ø Both rods and cones are photoreceptor cells of the center.
Ø Both can absorb photon (light)
Ø Both cells possess photoreceptor proteins to blot the photons (light).
Ø Both are modified nerve cells.
Ø Both rods and cones synapse with bipolar cells.
Ø The chemical process that supports phototransduction is similar in both cells.
Ø The outer segments of both cells possess membrane invaginations that contain the light absorbing pigments.
Difference betwixt Rods and Cones
| Sl. No. | Rod Cells | Cone Cells |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rod cells are located at the peripheral portion of the retina. | Cone cells are located at the central part (fovea) of the retina |
| ii | Rod cells are cylindrical and comparatively longer than cone cells | Cone cells are comparatively shorter than rod cells |
| iii | Rod cells are narrower than cone cells | Cone cells are usually wider than rod cells |
| 4 | More number of rod cells than cone cells | Number of cone cells are lesser than that or rod cells |
| 5 | Average number of rods in human is 120 million | Average number of cones in man is 6 1000000 |
| 6 | Rod cells are extremely sensitive to low levels of calorie-free | Cone cells are very dull sensitive to low light. Cone cells are very sensitive to bright light |
| 7 | Rod cells can be triggered even by a single photon of low-cal | Large number of protons is required to trigger the cone cells |
| eight | Rod cells help in scotopic vision (low calorie-free vision) and dark vision | Cone cells help in photopic vision (high calorie-free vision) daylight vision |
| 9 | Simply 1 type of visual pigment is present in rod cells | Three different types of visual pigments nowadays in cone cells |
| 10 | Rod cells possess very rapid regenerative ability | The regenerative power of cone cells is very less |
| 11 | In human, just a single type of rod jail cell is nowadays | In human, 3 distinct types of cone cells are nowadays based on their pattern of response to different wavelength of low-cal |
| 12 | The outer segment of rod jail cell is cylindrical and contains the paint rhodopsin | The outer segment of cone cell is cone shaped and contains the paint photopsin |
| 13 | Only one type of rhodopsin is present in rod cells | Three different types of photopsin, which respond differently with different wavelength of light (bluish, light-green and red), are present in cone cells to enable the colour vision |
| xiv | Rod cells are sensitive to scattered and direct light | Cone cells are sensitive only to direct light |
| 15 | The visual acuity of rod cells is less | The visual vigil of cone cells is high |
| 16 | Rod cells are absent-minded in fovea | Cone cells are full-bodied in the fovea |
| 17 | Loss of rod cells causes night blindness | Loss of cone cells causes legal incomprehension |
What Do Rod Cells Do,
Source: https://www.easybiologyclass.com/difference-between-rod-cells-and-cone-cells-comparison-table/
Posted by: nelsonbountly.blogspot.com



0 Response to "What Do Rod Cells Do"
Post a Comment